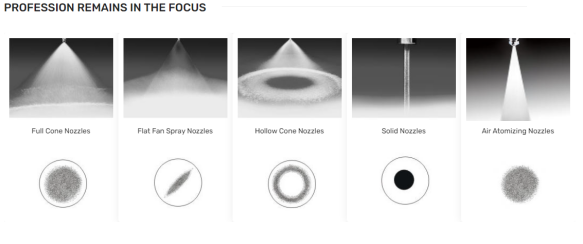
Industrial nozzle physical characteristics
1. Spray Efficiency
The nozzle is a mechanism that converts pressure into kinetic energy, and the spray efficiency of the nozzle must be determined by the kinetic energy of the liquid inside the nozzle. The larger the energy, the more pleasant the flow rate, in addition, because there is friction on the internal surface of the nozzle and the liquid itself, it leads to a loss of energy. Such a problem depends on the form of the nozzle and the quality of the processing, in general, the spray efficiency of the nozzle is about 55%-95%. The above information does not apply to air-assisted nozzles, because air-assisted nozzles must take into account numerous energy variables.
2. Spray Size
The size of atomizing droplets generated by the nozzle depends on the atomizing structure of the nozzle, the strength of liquid energy, the surface tension of the liquid and the density of the liquid, etc., because the size of the droplets after atomization is not completely consistent, therefore, the average spray particle size of the atomizing nozzle becomes an important data representing the size. In many nozzle application environments, the size of the spray particle size is usually very important, for example: the spray particle size in the application of waste gas cooling tower is very important, the particle size is too large, can not be completely evaporated within the established time, the unevaporated droplets into the cooling tower after the bag filter dust collector, will lead to poor effect or complete failure of the dust collector; On the contrary, droplets with too small particle size may not be able to cool the exhaust gas to a predetermined temperature range within a given time, and after the excessive high temperature exhaust gas enters the bag filter dust collector at the back of the extremely cold tower, it will not only burn the filter bag, but also may have a fire.
There are four expressions of spray particle size, of which the average particle size is the most commonly used, the average particle size refers to the ratio of droplet volume to surface area, commonly represented by D32, and in UM (micron) as a unit.
Mean particle size
Refers to the ratio of droplet volume to surface area, commonly represented by D32, which is the most commonly used reference data in the nozzle industry.
Quantity mean diameter
It is the average value obtained by adding the diameters of many measured droplets and dividing them by the total number of measured droplets.
Weight mean diameter
It is the sum of all measured weights, divided by the total measured amount and converted to the average diameter.
Intermediate diameter of quantity
It means that 50% of the droplet falls in diameter, half of the spray droplet is larger than this diameter, and half of the spray droplet is smaller than this diameter
3. Spray Angle
When spraying is carried out, the Angle Angle closest to both sides of the spray amplitude is called the "spray Angle". The spray Angle and the spray distance (the distance from the nozzle to the spray) are related to the size of the spray coverage area.
4. Traffic Distribution
In order to adapt to a variety of different environmental requirements, engineers in the design of nozzles, give each nozzle has different flow distribution characteristics, flow distribution can be divided into: Standard convex distribution, uniform distribution, concave distribution and unit distribution four, the different design is mainly to make the nozzle in the single use or complex collocation, can achieve the best uniformity and impact force, in the following figure, a detailed description of the various styles of nozzle flow distribution and spray profile.